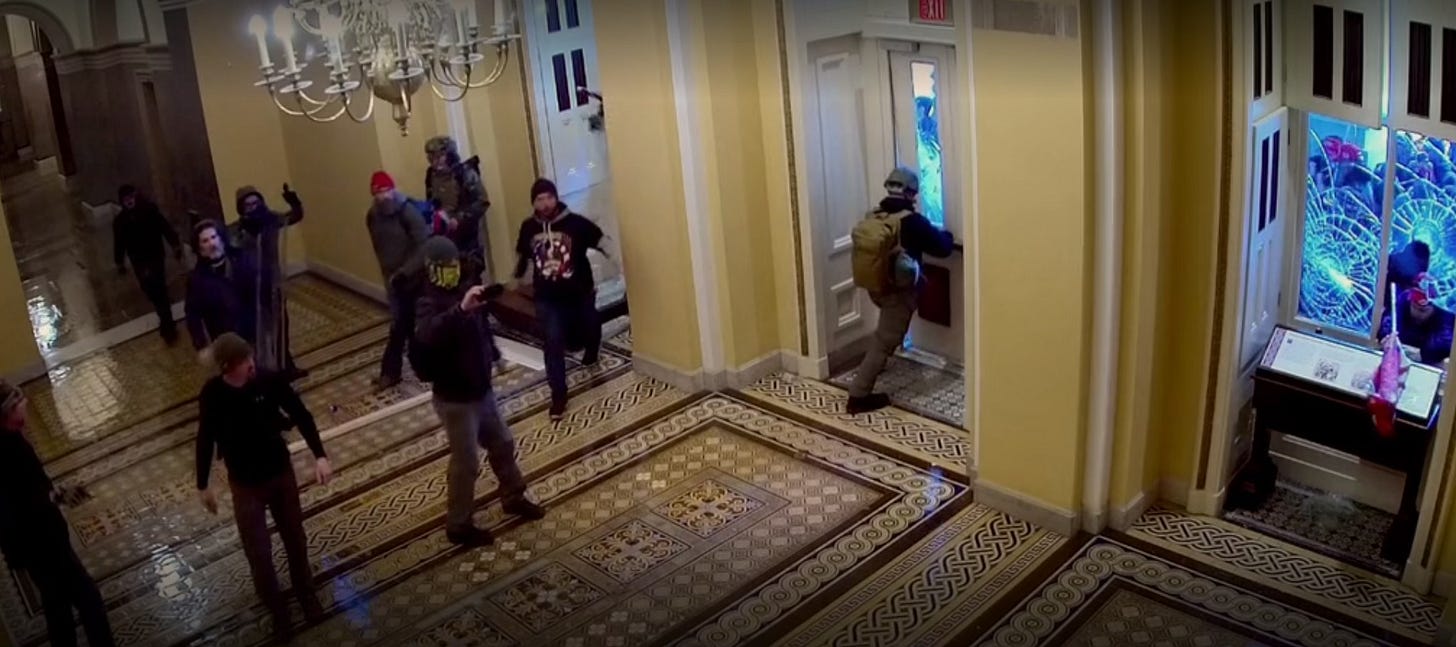This Day in Legal History: January 6 Insurrection
On January 6, 2021, a significant and unprecedented legal and constitutional crisis unfolded in the United States. As a joint session of Congress convened to certify the Electoral College results of the 2020 presidential election, a mob of supporters of then-President Donald Trump stormed the U.S. Capitol. The attack followed weeks of false claims about election fraud and a rally earlier that day in which Trump urged his supporters to “fight like hell.” The violent breach forced lawmakers to evacuate, delayed the certification of Joe Biden’s victory, and resulted in deaths, injuries, and extensive property damage.
Legally, the event triggered a cascade of consequences. Hundreds of participants were arrested and charged with offenses ranging from unlawful entry and assaulting federal officers to seditious conspiracy. High-profile members of far-right groups like the Oath Keepers and Proud Boys were prosecuted, with some leaders convicted of seditious conspiracy, a Civil War-era charge rarely used in modern times. The attack also led to Trump’s second impeachment, the first time in U.S. history a president was impeached twice. He was charged with incitement of insurrection, although the Senate ultimately acquitted him.
In the broader legal aftermath, January 6 prompted legislative and judicial scrutiny of the Electoral Count Act of 1887, with Congress passing reforms in 2022 to clarify the vice president’s limited role in certifying election results. The attack also raised questions about the limits of First Amendment protections when political speech turns into violent action, and about the potential disqualification from office under Section 3 of the 14th Amendment, which prohibits insurrectionists from holding public office.
Barry Pollack, the U.S. attorney best known for securing WikiLeaks founder Julian Assange’s release deal, is now representing Venezuelan president Nicolás Maduro in a high-profile U.S. narcotics case. Maduro, who was captured in a U.S. military operation along with his wife, pleaded not guilty this week in a Manhattan federal court to charges of leading a cocaine trafficking conspiracy involving guerrilla groups and drug cartels. Pollack plans to challenge the legality of Maduro’s capture—calling it a “military abduction”—and is also expected to raise arguments about foreign leader immunity.
These arguments face steep legal obstacles. The U.S. no longer recognizes Maduro as Venezuela’s legitimate president, having rejected the results of his 2018 re-election. Furthermore, U.S. courts have historically been reluctant to dismiss cases based on how a defendant was brought to U.S. soil. Still, Pollack’s involvement signals a serious defense strategy grounded in international legal questions and executive immunity claims.
Pollack’s experience with politically charged and internationally sensitive cases is extensive. He recently helped negotiate Assange’s release from a British prison through a plea deal that allowed the WikiLeaks founder to avoid U.S. imprisonment and return to Australia. His track record also includes work on behalf of a former CIA officer and an acquitted Enron executive.
Assange’s lawyer Barry Pollack to fight Maduro’s US narcotics charges | Reuters
With a new Republican majority appointed by President Donald Trump, the National Labor Relations Board (NLRB) is expected to shift sharply away from pro-union policies that defined its recent Democratic era. After nearly a year of paralysis caused by Trump’s unprecedented firing of Democrat Gwynne Wilcox—leaving the board without the quorum needed to issue decisions—the Senate confirmed two Republican nominees in December 2025, restoring its ability to act and giving conservatives control of the five-member board for the first time since 2021.
Key Biden-era decisions are now vulnerable to rollback. These include expanded union rights such as representation without secret-ballot elections, bans on mandatory anti-union employer meetings, and broader remedies for fired workers. Critics say these moves strayed from precedent; federal courts are reviewing them, but outcomes will vary by jurisdiction unless the Supreme Court weighs in.
Union election rules are also likely to change. Under Biden, the NLRB accelerated the election process and made it harder for decertification efforts to proceed—moves unions supported to counter employer delays. Republicans are expected to reverse these rules, potentially making it easier to dissolve existing unions.
The board’s political independence is also under scrutiny. A court recently upheld Trump’s removal of Wilcox, challenging legal protections meant to shield NLRB members from dismissal without cause. If the Supreme Court supports similar arguments in upcoming cases, the NLRB’s structural independence could be weakened, raising concerns about politicization and fairness in labor adjudications.
Meanwhile, lawsuits by major companies like Amazon and SpaceX are targeting the board’s role as both prosecutor and judge in its own cases, claiming constitutional violations. If courts side with these challengers, it could force Congress to restructure the agency—perhaps by limiting its powers or shifting cases to federal courts.
NLRB poised for major policy shifts in 2026 with new Trump-appointed majority | Reuters
Wisconsin Judge Hannah Dugan resigned following her conviction for obstructing the arrest of a migrant in her courtroom, a case that became entangled in broader national tensions over immigration enforcement. Dugan, elected to the Milwaukee County Circuit Court in 2016, was found guilty in December 2025 of helping Eduardo Flores-Ruiz, a Mexican national facing domestic violence charges, evade U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) agents who were present at the courthouse. She had denied wrongdoing, claiming she followed a courthouse policy requiring staff to notify supervisors of ICE’s presence.
Her conviction drew sharp criticism from Republican lawmakers, with some calling for impeachment, especially as the Trump administration intensifies efforts to crack down on local interference with federal immigration policy. Dugan had been suspended from her judicial duties during the legal proceedings. Prosecutors framed the case as a warning that public officials are not above the law, highlighting the Justice Department’s willingness to pursue charges against judges who obstruct federal enforcement actions.
Before serving as a judge, Dugan led a local Catholic Charities chapter that provided refugee resettlement services. Her background and the nature of the charges underscored the ongoing conflict between local protections for immigrants and federal efforts to expand deportations.
Wisconsin judge resigns after being convicted of obstructing migrant arrest | Reuters
My column this week is on a novel cruise tax. Hawaii’s attempt to expand its transient accommodations tax to include cruise ship passengers hit a temporary roadblock when the 9th Circuit Court of Appeals issued a New Year’s Eve stay, pausing enforcement of the new “green fee.” The law, which took effect January 1, aims to place cruise cabins on equal tax footing with hotels by imposing an 11% tax on the portion of a cruise fare linked to overnight stays while docked in Hawaiian ports. Hawaii argues this is a general, nondiscriminatory tax on short-term lodging rather than a fee tied to the ship itself. To bolster its legal case, the state is framing cruise cabins as equivalent to hotel rooms, and emphasizing that the tax is based on services consumed on land, not the ship’s movement or port access.
The cruise industry, however, contends the tax violates the Constitution’s Tonnage Clause, which prohibits states from levying duties on ships for merely entering or staying in port. They’ve also invoked the Rivers and Harbors Appropriation Act of 1884, which restricts port-related charges not linked to specific services. But Hawaii’s defense is that the tax is not about access or vessel status—it is a consumption tax on guests staying overnight, regardless of whether the bed is on land or in a moored ship. The policy avoids targeting ships and instead captures revenue from tourism, aligning maritime and land-based lodging under a consistent legal framework.
The Department of Justice has joined the cruise industry’s challenge, suggesting the issue’s seriousness. If litigation continues, the U.S. Supreme Court may ultimately decide whether this tax model is constitutionally sound. Still, Hawaii’s approach—drafting a neutral, consumption-based tax rather than a maritime-specific charge—may serve as a blueprint for other coastal states looking to tap into cruise tourism revenue without triggering constitutional violations.